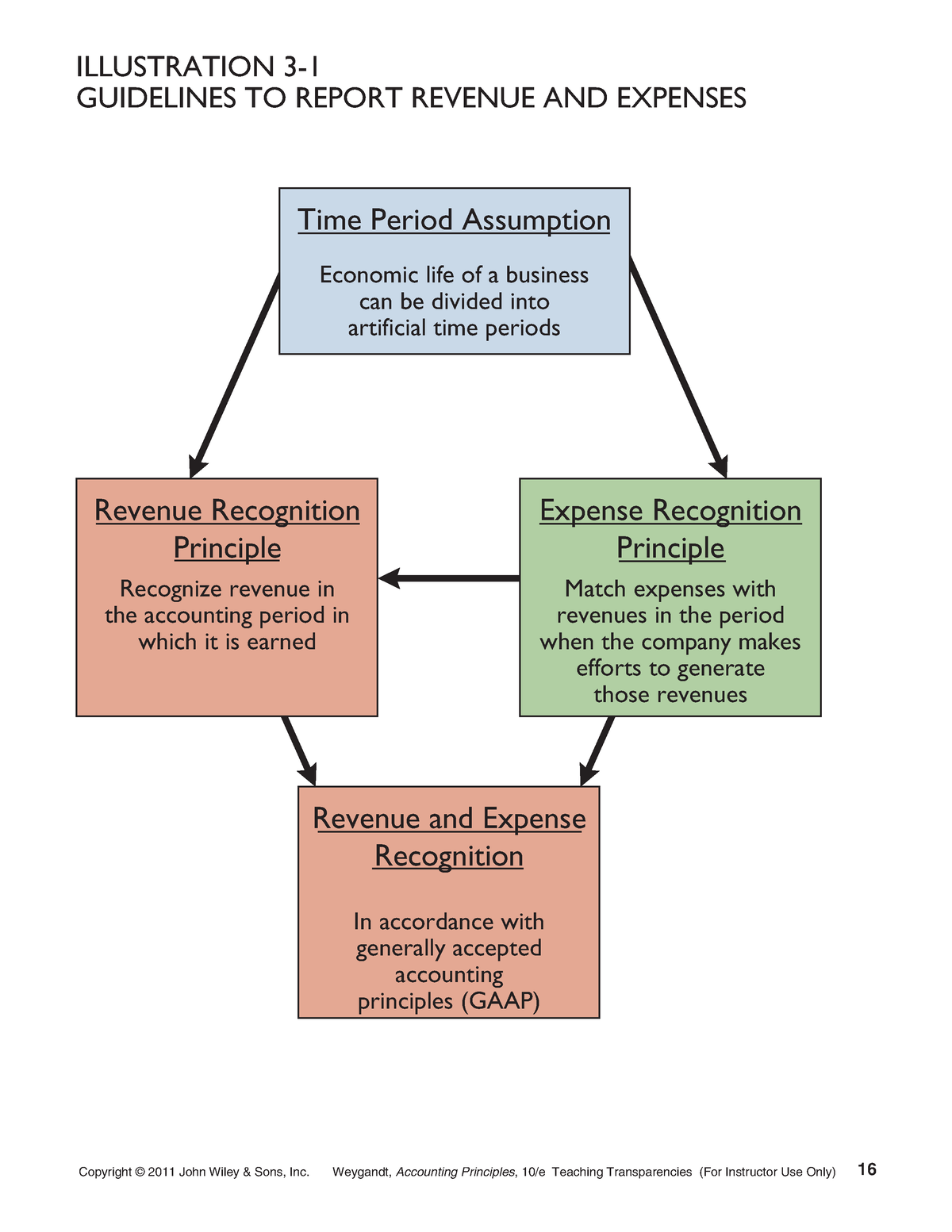
The basic accounting principles serve as bases in preparing, presenting and interpreting financial statements. They lay down the foundations to prevent misunderstandings between and among the preparers and users of financial statements. Under the Economic Entity Assumption, the accounting records of a business must be kept separate from the personal financial records of its owner or employees. Mixing personal transactions with the company’s business transactions will negatively affect the fair presentation of information in the financial statements and lead to distorted amounts. From an operational standpoint, the time period assumption aids management in budgeting, forecasting, and decision-making.
Other Principles Derived from the Above Concepts
Therefore, the importance of the time period principle is to inform any readers about the time period for which the financial statements have been prepared. Investors and analysts, on the other hand, still rely heavily on periodic reports to assess company performance. However, they are increasingly supplementing these reports with alternative data sources that provide more current insights into a company’s operations and financial health. Business leaders and managers are also reconsidering the time period assumption in light of the demand for more timely and relevant financial information. The rise of big data analytics allows for more dynamic and predictive financial analysis, which could shift the focus from historical reporting to forward-looking financial insights. It is stated that the total revenue is $100 million, but there is no information provided regarding how it was collected or which months were particularly successful or failed.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Presentation of the Time Period in Financial Statements
- Creditors, on the other hand, use financial statements to evaluate the risk of lending to a business.
- If a company chooses to defer revenue recognition, it may appear less profitable in the short term, potentially affecting stock prices and investor confidence.
- The realization principle, on the other hand, stipulates that revenue should only be recognized when it is earned and realizable, regardless of when cash is received.
The matching principle, for example, requires that expenses be matched with the revenues they help to generate, which prevents companies from overstating profits in a given period. From a manager’s point of view, this synthesis aids in performance evaluation and decision-making. Managers rely on periodic financial statements to assess the company’s performance and make informed decisions. They need to understand the implications of these accounting principles to interpret the financial statements correctly. If it recognizes revenue only upon project completion, its financial statements might show no revenue for several periods followed by a large influx once a project is finished. This can mislead stakeholders about the company’s ongoing financial health and operational efficiency.
It allows for the comparison of financial results across different periods, highlighting trends and areas for improvement. For investors and creditors, this assumption provides a consistent basis for analyzing a company’s financial stability and profitability over time. Regulatory bodies and tax authorities also rely on this assumption to ensure compliance with laws and regulations.

The Significance of Time Period Assumption in Modern Accounting
For instance, if a company delivers a product in one fiscal period but receives payment in another, accrual accounting recognizes the revenue at the time of delivery. This method provides a more accurate financial picture, as it aligns income and expenses consignment sale definition with the time period in which they are incurred. By exploring the Realization Principle from these various angles, we gain a comprehensive understanding of its significance in the accounting world and its impact on financial reporting and analysis.
It is one of a number of fundamental accounting rules and principles that is common to cash basis accounting, accrual basis accounting and their modifications. From an accounting perspective, the time-based revenue recognition model is increasingly being scrutinized for its ability to deal with these complexities. The model requires that revenue be recognized when it is earned and realizable, which is often interpreted as over the time the service is provided or the product is used. However, this can lead to revenue being reported in a way that does not align with the actual value delivered to the customer.
The Time Period Assumption is a cornerstone of financial reporting that enables businesses to present their financial activities in a clear, consistent, and comparable manner across different time periods. It supports various stakeholders in making informed decisions and upholds the integrity of financial information. A year-end income statement shows the income and expense performance for the company for the entire year. The balance sheet, on the other hand, only shows a picture of the company on a single date in time.
Investors also benefit from this assumption as it provides them with regular updates on a company’s financial health, allowing them to make timely investment decisions. A savvy investor might use annual reports to analyze a company’s year-over-year growth and decide whether to buy, hold, or sell their shares. Consider a company that decides to change its fiscal year-end from December 31st to March 31st to better align with its business cycle. This change would require an interim financial statement covering the three-month transition period, which would then be used to adjust the comparisons in subsequent annual reports. To maintain comparability, companies making a transition from one fiscal year to another or those operating in industries with non-standard fiscal periods may need to make adjustments. These adjustments ensure that financial statements reflect a full year’s performance and are comparable year over year.
Time period assumption permits the accountant to measure the performance of businesses and other economic entities. If time is not divided into distinct periods, the accountant cannot record separate transactions in separate time periods. If transactions are not recorded in separate time periods, the accountant cannot compile and compare transactions against one another to measure various aspects of the business’ activities. To illustrate these points, consider a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company that offers annual subscriptions. The company receives payment upfront, but according to the realization principle, it must recognize the revenue proportionally each month as the service is provided. This approach not only adheres to the time period assumption but also provides a more accurate representation of the company’s earnings throughout the year.
By breaking down operations into manageable intervals, managers can set targets, monitor progress, and make timely adjustments to strategies and operations. Investors and analysts are also advocating for more frequent updates, arguing that the traditional quarterly reports are too infrequent to make informed decisions in today’s fast-paced market. They point to companies like Alphabet Inc., which releases real-time traffic and advertisement data, providing insights into the company’s performance well ahead of quarterly reports. From an investor’s standpoint, the timing of revenue recognition can significantly affect a company’s reported earnings and, consequently, its stock price.
